CLIPtheCenter
GitHub Link
Master Thesis Report
Master Thesis Presentation
Most modern machine learning techniques based on neural networks need large amounts of well-annotated training data to demonstrate outstanding performance. However, obtaining instance-level annotations like object bounding boxes in real-world settings is tedious, and it is still a significant challenge in many industrial applications of neural networks. Additionally, the distribution of classes in real-world datasets is inherently imbalanced. This thesis deals with the challenge of few-shot object detection. Given a set of base classes with abundant labeled data and a set of novel classes with few support images, this thesis aims to devise algorithms that can predict and classify the object instance belonging to both the base and novel classes in a query image.
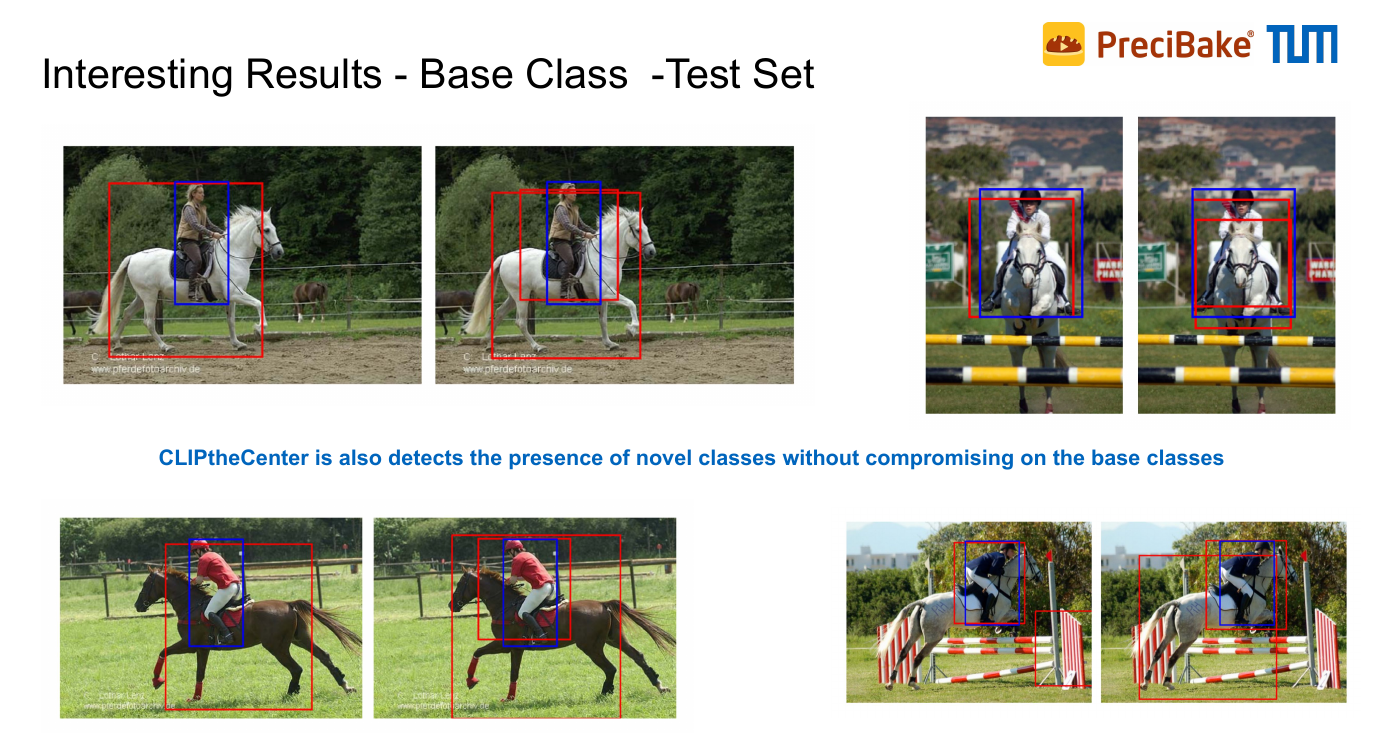
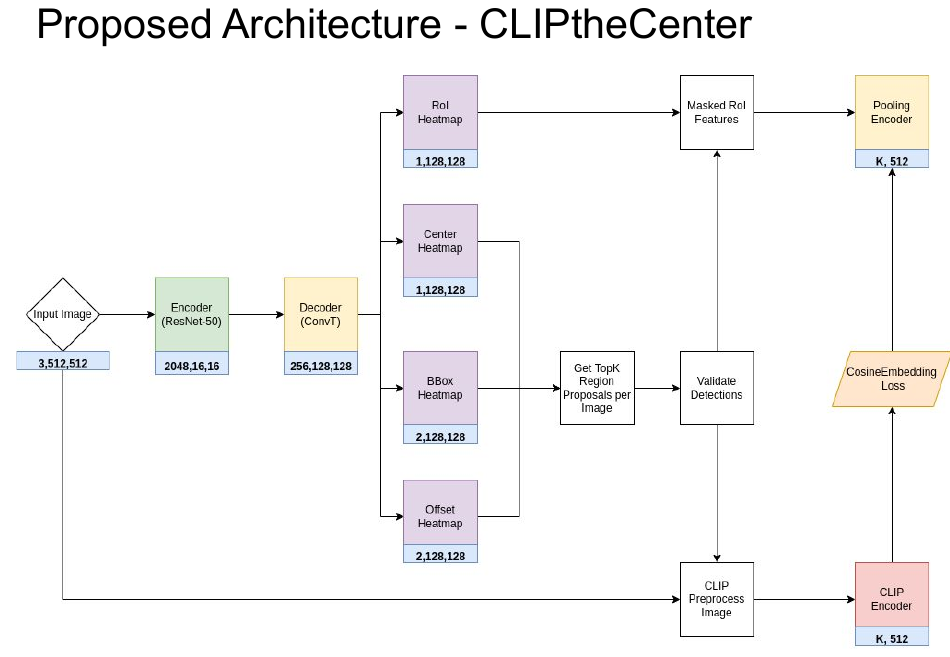
In the first part of the thesis, a representative multi-modal model CLIP as well as a self-supervised model, DINO, are experimented with to test the efficacy of different pretraining strategies. Then, algorithms based on class codes are introduced to classify the query image into target novel classes. Finally, experiments were performed on CUBS 200 dataset. With the proposed classification algorithm, the CLIP encoder demonstrated strong few-shot capability with just ten support images a class and competed with a fully supervised ResNet-50 model. In the second part of the thesis, a novel few-shot object detector CLIPtheCenter is designed that extends CenterNet for the task of few-shot object detection. Generalization experiments are performed on a dataset consisting of fifteen base classes and five novel classes from the PASCAL VOC dataset . As a result, CLIPtheCenter doubled the class agnostic detection performance compared to a vanilla CenterNet in this base class splits. Furthermore, when classification performance is also taken into account, CLIPtheCenter tripled the performance of the CenterNet on the base classes split when CLIP Encoder-based class codes are used for class assignments. Finally, ablation studies verified the underlying intuitions for these performance gains.
Architecture
Sample Results